Table of Content
This is a summary of ACM TechTalk by Sebastian Raschka by Mahdee Kamal
Ways to Use LLMs
- Public/proprietary services (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini).
- Running LLMs locally.
- Setting up private APIs.
LLM Development Stages
- Building: Coding the architecture and preparing the dataset.
- Pre-Training: Training the LLM as a deep neural network.
- Fine-Tuning: Customizing the pre-trained model for specific tasks.
How LLM Works
- An LLM model is simply (pre)trained to predict the next word/token. LLMs generate text iteratively, one word at a time.
- Input is prepared as sliding windows over text. Batching is used for faster training.
- LLMs are trained on vast datasets (GPT-3 : 0.5T, LLaMA-1 : 1.4T, LLaMA-3 15T tokens). There is a trend toward both scaling up and improving data quality.
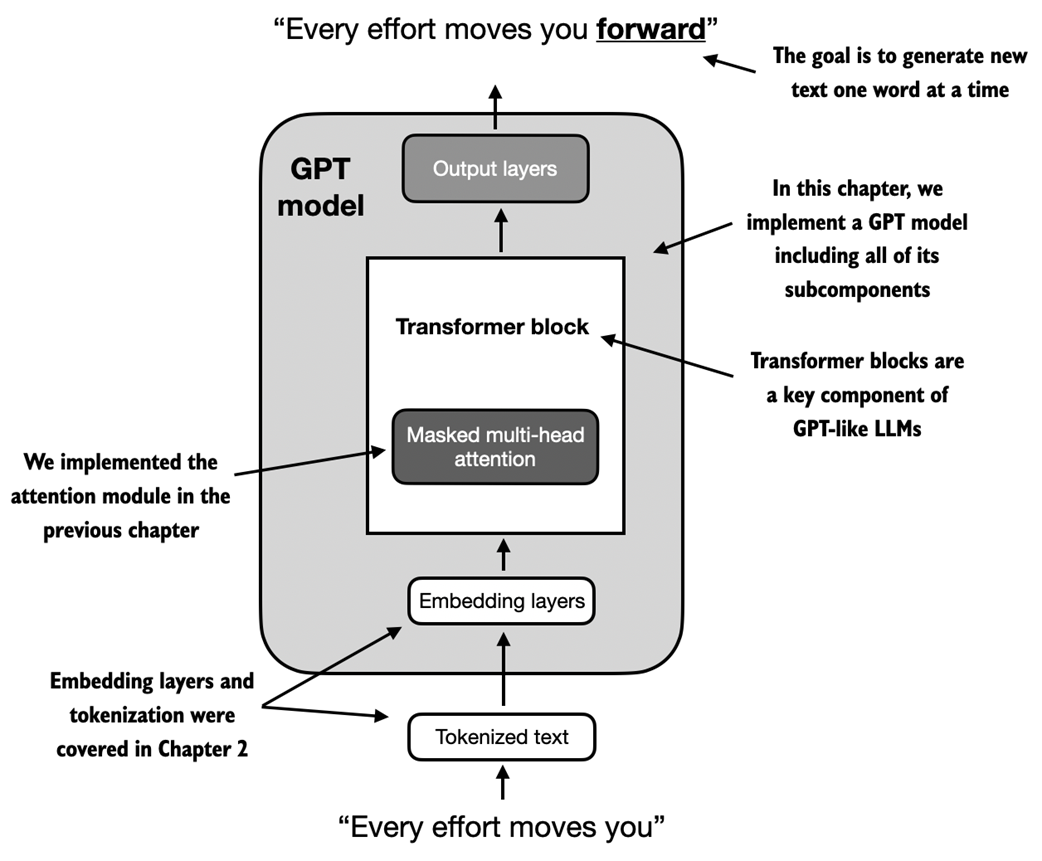
LLM Architecture
- LLMs typically use a Transformer architecture, with key components including tokenization, embedding layers, and a masked multi-head attention module.
- All the different LLMs have mostly the same architecture. They may differ in dropout, activation function & normalization. Eg: RMSNorm, rotational positional embeddings instead of absolute embeddings.
- For different GPT variables are
- Number of parameteres
- Number of times the transformer block is repeated
- Number of heads in multi-head attention model.
- Number of dimension of the embeddings
Detailed Architecture:
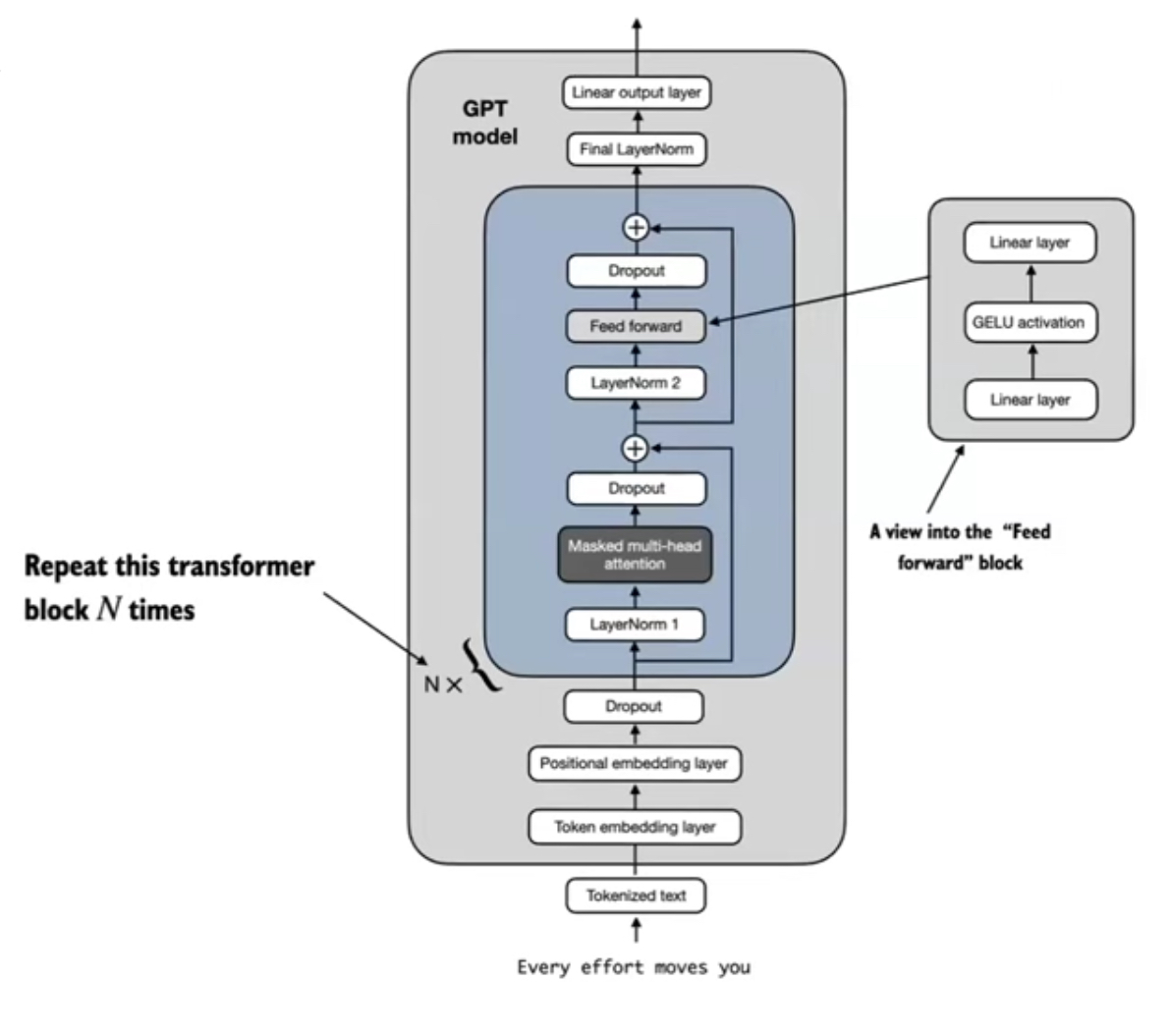
SImplified Version: source
Pre-training Process
- Pre-training involves a standard deep learning training loop with cross-entropy loss and Adam optimizer.
- Key challenges: Scaling the training process with multiple GPU, involves multiple machines due to the massiveness of model & dataset.
- Labels are the inputs shifted by +1 Ex: [In the heart of ] —> [the heart of the]
- Epochs: 1-2 epochs is usually a sweet spot.
Due to the resource-intensive nature of pre-training, existing pre-trained models like LLaMA are often used as a base for further fine-tuning.
Fine-tuning Process
We only fine-tune the last few layers.
Usecase Classifier:
- Replacing the output layer with a smaller one that suits the specific task (e.g., spam vs. non-spam)
Usecase Personal Assistant:
- For building chatbots or personal assistants, instruction fine-tuning is used, where the model is trained on a dataset containing instructions and desired responses.
- A prompt style template is applied to the dataset to guide the LLM in following instructions.
Evaluating LLMs
- MLU (Massive Multitask Language Understanding) is a multiple-choice benchmark
- HellSwag and TruthfulQA
- AlpacaEval
- Chatbot Arena (Based on Userfeedback)
Q&A
- Fav tool to run LLM locally? - Lama
- How start-ups fine-tunes the weights and biases of an OpenAI GPT? - Not possible, they uses prompt engineering.
- What is more effective: continuing training a foundational model or developing a Q&A dataset for fine-tuning? - Both approaches work; it’s an open research problem, but Q&A data can provide context-efficient fine-tuning.
- A little bit more about attention? - read on your own
